Understanding Emphysema and COPD
As a blogger, I find it essential to discuss the connection between emphysema and COPD. Many people are unaware of the differences and similarities between these two conditions, and understanding them can help to better manage and treat their symptoms. In this section, we will delve into the basics of emphysema and COPD, so that you can have a better understanding of these respiratory diseases.
What is Emphysema?
Emphysema is a progressive lung disease that damages the air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs, making it difficult to breathe. This damage causes the walls of the air sacs to lose their elasticity, resulting in less oxygen being exchanged in the bloodstream. Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and is primarily caused by smoking, although other factors such as air pollution and genetic predisposition may also play a role.
What is COPD?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a term used to describe a group of lung diseases that cause airflow blockage and breathing difficulties. The most common conditions that fall under the umbrella of COPD are emphysema and chronic bronchitis. COPD is a progressive disease, meaning that it worsens over time, and it is the third leading cause of death worldwide. Like emphysema, the primary cause of COPD is smoking, but other factors such as air pollution, occupational exposure, and genetic factors can also contribute to the development of the disease.
How Emphysema and COPD Are Connected
As mentioned earlier, emphysema is a type of COPD, which means that the two conditions are inherently connected. Emphysema and chronic bronchitis, another type of COPD, often coexist in individuals who have been diagnosed with COPD. The primary connection between these two conditions is that they both involve damage to the lungs and airflow obstruction, leading to breathing difficulties.
Signs and Symptoms of Emphysema and COPD
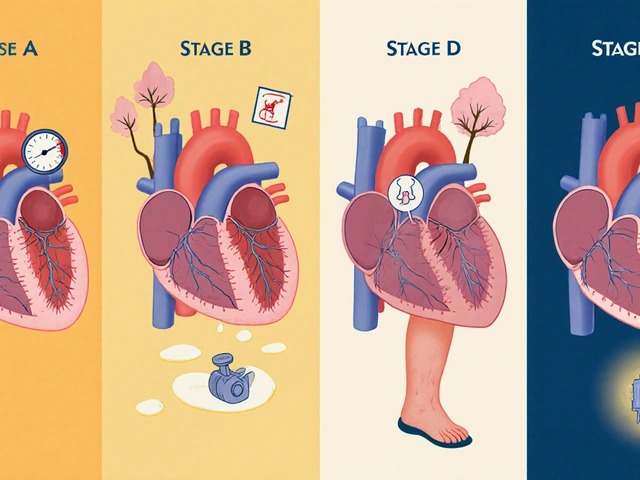
Although emphysema and COPD share many similarities, they also have some distinct symptoms. Some common signs and symptoms of emphysema and COPD include shortness of breath, chronic cough, wheezing, chest tightness, and frequent respiratory infections. However, emphysema is more likely to cause weight loss and a barrel-shaped chest due to the increased size of the lungs, while chronic bronchitis is characterized by a persistent cough that produces mucus. It is important to note that these symptoms may vary from person to person and may not always be present.
Diagnosing Emphysema and COPD
Diagnosing emphysema and COPD typically involves a combination of tests and a thorough medical history. Your doctor may perform a physical examination, ask about your smoking history, and use tests such as spirometry, chest X-rays, or CT scans to assess the structure and function of your lungs. Blood tests may also be used to determine how well your lungs are exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide. Early diagnosis is crucial in managing the symptoms and progression of both emphysema and COPD.
Treatment Options for Emphysema and COPD
While there is no cure for emphysema or COPD, there are several treatment options available to help manage symptoms and slow the progression of the disease. These treatments may include medications such as bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, and oxygen therapy. Lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, avoiding lung irritants, and participating in pulmonary rehabilitation can also help improve the quality of life for individuals with emphysema or COPD. In severe cases, surgical interventions such as lung volume reduction surgery or lung transplantation may be considered.
Managing Emphysema and COPD
Managing emphysema and COPD requires a combination of medical treatment and lifestyle changes. It is important to work closely with your healthcare team to develop a comprehensive management plan that includes medication, exercise, breathing techniques, and nutritional support. Additionally, it is crucial to avoid exposure to lung irritants, such as tobacco smoke, air pollution, and occupational hazards. By taking an active role in managing your condition, you can help to slow the progression of the disease and improve your overall quality of life.
Preventing Emphysema and COPD
Preventing emphysema and COPD involves taking steps to reduce your risk factors, such as quitting smoking, avoiding exposure to lung irritants, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and routine medical check-ups can also help to keep your lungs healthy and reduce your risk of developing these conditions. While these preventive measures may not guarantee that you will never develop emphysema or COPD, they can significantly lower your chances and help to maintain your overall health.



May 12, 2023 AT 01:01 AM
I’ve been researching this for my dad-he’s been a smoker for 40 years and just got diagnosed. The way you broke down the difference between emphysema and COPD actually helped me understand why his oxygen levels drop so fast. It’s not just ‘bad lungs,’ it’s structural damage. Thanks for the clarity.
May 12, 2023 AT 08:25 AM
People need to stop pretending smoking is a personal choice when it wrecks the healthcare system. My brother died of COPD at 52. This isn't a 'lifestyle'-it's a preventable tragedy. Quit now or stop acting like you're innocent.
May 12, 2023 AT 13:29 PM
Fascinating! 🤓 The pathophysiological cascade involving elastase-antielastase imbalance-particularly in alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency-is often under-discussed in layman’s forums. I mean, truly, the pulmonary parenchymal destruction is a masterpiece of biological decay… 🫁💔
May 13, 2023 AT 18:14 PM
I had this same diagnosis last year. I didn’t realize how much weight loss was tied to it until my nutritionist said, ‘Your body’s burning calories just trying to breathe.’ I lost 30 lbs in 4 months. No one warned me.
May 14, 2023 AT 14:14 PM
you guys are so dumb its not even funny. its not emphysema its just smoking. you dont need a fancy word for it. its just lungs getting wrecked. stop making it sound like a medical mystery. its cigarette ash.
May 15, 2023 AT 11:33 AM
I’m from Sydney. We’ve got this massive anti-smoking campaign here-billboards, taxes, plain packaging. It works. My mum quit at 58. She’s breathing better now. It’s not magic. It’s just… not smoking.
May 16, 2023 AT 20:09 PM
If you’re reading this and you’re worried about your breathing, please don’t wait. Pulmonary rehab changed my life. It’s not just exercise-it’s learning how to breathe again. Your body remembers how. You just have to show up. I’m here if you want to talk.
May 18, 2023 AT 00:04 AM
Spirometry remains the gold standard. FEV1/FVC ratio < 0.7 confirms obstruction. No imaging is required for diagnosis.
May 19, 2023 AT 21:53 PM
My cousin in Melbourne got a lung transplant at 41. He was a smoker for 22 years. Now he runs marathons. It’s not a cure, but it’s a second chance. Don’t wait till you’re on oxygen.
May 20, 2023 AT 21:55 PM
The systemic inflammatory burden in COPD is profound-elevated CRP, IL-6, TNF-alpha-this isn’t just a lung disease. It’s a multisystem disorder. Early intervention with anti-inflammatories and pulmonary rehab can alter trajectory.
May 21, 2023 AT 04:42 AM
Why are we even talking about this? Just quit smoking. That’s it. No science needed.
May 22, 2023 AT 00:41 AM
i hate how peopel think they know evrything about lung disaese. i had bronchitis and they called it copd. its not the same. stop misdiagnosing people.
May 22, 2023 AT 04:28 AM
I got my first inhaler last month. I used to think I was just out of shape. Turns out I was breathing through a straw. 🤯 My dog even noticed I stopped wheezing at night. He’s been happier.
May 24, 2023 AT 04:28 AM
This post is helpful. I’ve got a friend in India who’s never heard of COPD. She thinks coughing all day is normal. Maybe we need more of this in local languages.
May 24, 2023 AT 06:22 AM
COPD is just a label for smokers who refuse to quit.
May 25, 2023 AT 00:14 AM
I was diagnosed at 29. I didn’t smoke. My dad did. They said it was genetic. Now I’m on oxygen 24/7. This isn’t about choices. It’s about fate. And it’s terrifying.